-
Introduction
IUI is an effective simple non- invasive, cost effective technique having success rates between natural intercourse and IVF-ET. The sperm travel lesser distance which increases the number of spermatozoa available to oocyte by 25%. The method is almost invariably employed for women with patent tubes and in the absence of severe male factor.
HistoryThe recorded IUI in humans was performed in 18th century. Dr John Hunter and his nephew achieved first pregnancy and delivery in London. However, the procedure could not make much headway until 1970s due to difficulties faced in semen preparation of improved quality. Today it is used as a routine procedure..
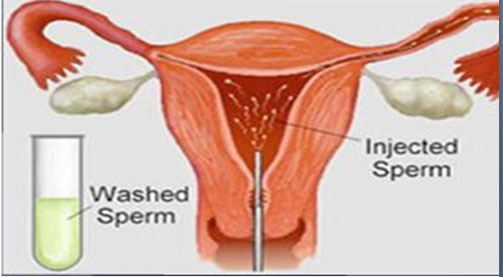
DefinitionIUI is a direct placement of processed highly motile concentration of sperm, washed free of seminal plasma and other debris, into the uterine cavity at any point above the internal OS. This process bypasses the cervical barrier and sperm is placed directly inside the uterus closer to the fallopian tube, at the time of expected egg release to increase the chance of fertilization resulting in higher chance of conception. The follicle development is monitored by trans viginal sonography
Indications for IUI The major indications are:
 Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia with Count <20 million/ml>10 million/ml
Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia with Count <20 million/ml>10 million/ml Cervical Factor
Cervical Factor Unexplained Infertility
Unexplained Infertility-
 Minimal Endometriosis
Minimal Endometriosis -
 Ejaculatory Failure
Ejaculatory Failure  Immunological Factor
Immunological Factor Cryopreserved Sample
Cryopreserved Sample-
 Donor Insemination
Donor Insemination
The rationale of performing IUI is to overcome the problem of
 Vaginal Acidity
Vaginal Acidity-
 Cervical Mucus Hostility
Cervical Mucus Hostility -
 Deposition of a good number of high motile and morphologically normal sperm in uterus
Deposition of a good number of high motile and morphologically normal sperm in uterus
IUI may be coupled with stimulated ovaries. Stimulation of the ovaries result is production of more than one oocytes, which improve the chances of fertilization and subsequent establishment of pregnancy in sub fertile couple.
Timing of InseminationThe timings of insemination is decided according to whether the insemination is to be carried out once or twice.
- Single Insemination: IUI is carried out within 36 to 40 hours after triggering ovulation with hCG injection.
- Double insemination: is carried out around 24 and around 48 hours after hCG injection.
Patient is instructed to clean his genital organs thoroughly and produce semen by masturbation after three to five days of ejaculation absentence (semen collection in hospital is preferable but if you are not comfortable with that, semen can be collected at home and then transported to the hospital).
Sterilized wide mouth non-toxin sealed container is given to the patient and is instructed to write his name and registration number carefully.
You is instructed to ejaculate the whole semen specimen from the first to the last droplet into the container. If any portion of it falls outside, you are is advised to neglect it and report it to the service provider.
Semen contains a large amount of other unwanted material over and above sperm. Only sperm can be injected in to the uterus. The semen sample is processed in laboratory in such a way so as to remove every unwanted substance and separate the best motile and morphologically normal sperm out of the semen sample
Frozen semenIt can be used for insemination if
 Husband can not remain present on the day of insemination.
Husband can not remain present on the day of insemination. Husband can not perform and collect semen on demand.
Husband can not perform and collect semen on demand. If husband is undergoing medical or surgical treatment which can adversely affect the sperm production.
If husband is undergoing medical or surgical treatment which can adversely affect the sperm production. Cryoaccumulation - freezing multiple semen samples and then using them together at one time.
Cryoaccumulation - freezing multiple semen samples and then using them together at one time. For using frozen semen, husband can freeze his semen at any convenient time. Once frozen, semen can be preserved and used after any duration of time up to 10 yrs.
For using frozen semen, husband can freeze his semen at any convenient time. Once frozen, semen can be preserved and used after any duration of time up to 10 yrs.
 Inadequate sperm count.
Inadequate sperm count.-
 If the transport of sperm to the oocyte through the cervical mucus is defective.
If the transport of sperm to the oocyte through the cervical mucus is defective. -
 A couple with unexplained infertility.
A couple with unexplained infertility.
To have optimal chances with IUI treatment in Amritsar, the female should be under 30 years of age, and the man should have a sperm count of more than 10 million per ml. The tentative pregnancy rate varies from 15-20% per cycle. As the technique is more cost effective and less stressful than IVF-ET, this method is almost invariably employed for women with patent tubes and in the absence of severe male factor infertility.
Legal Issues- Husband is the father of the child in all respects.
- Child conceived is fully legitimate.
- The frozen sample is to be used exclusively for donor’ wife.
- Use of semen after the death of husband is lawfully allowed, and the child so born will carry the name of father.
DI uses sperm from a donor to help the woman become pregnant. However, before proceeding to DI, parenting role, alternate methods to DI, emotional, psychological, legal, religious and cultural issues should be thoroughly discussed leaving the choice entirely to the patient couple.
Break Period--A minimum time up 3 months is given to the couple to reconcile before proceeding with DI. The couple may be referred to Professional Counselor.
Who need Donor Insemination? Male infertility treatment in Amritsar.
-
 Azoospermia
Azoospermia -
 Congenital absence of vas deferens.
Congenital absence of vas deferens. -
 Previous vasectomy.
Previous vasectomy. -
 Low sperm count.
Low sperm count. -
 Anti sperm- antibodies
Anti sperm- antibodies -
 Sexual dysfunction.
Sexual dysfunction. -
 Couple who does not wish to undergo IVF/ICSI.
Couple who does not wish to undergo IVF/ICSI.
-
 Autosomal dominant genetic disorder in male.
Autosomal dominant genetic disorder in male. -
 Recessive genetic trait in both partners
Recessive genetic trait in both partners -
 The couple has Rh
The couple has Rh
-
 Lesbian couples.
Lesbian couples. -
 Single women.
Single women.
-
 It is a responsibility of the ART clinic to procure sample.
It is a responsibility of the ART clinic to procure sample. -
 Appropriate Sperm banks are the only Authorized Suppliers. Sperm donors are screened for sexually transmitted diseases and some genetic disorders.
Appropriate Sperm banks are the only Authorized Suppliers. Sperm donors are screened for sexually transmitted diseases and some genetic disorders. -
 Sperm donation by relative or friends is not permitted.
Sperm donation by relative or friends is not permitted. -
 The identity of the donor will be kept confidential.
The identity of the donor will be kept confidential. -
 All records of sperm received, stored and supplied will be kept by the ART bank.
All records of sperm received, stored and supplied will be kept by the ART bank.
Donor Matching Before the use, the patient is consulted for the choice of physical features. Bank is required to supply the information regarding age, height, weight, educational qualification, profession, family background, and any known disease carrier status. Efforts are made to match the features with the husband. The factors taken care of are:
-
 Physical characteristic (eye colour, hair colour and skin colour etc.)
Physical characteristic (eye colour, hair colour and skin colour etc.) -
 Blood group
Blood group -
 Rh
Rh
For Single Woman
-
 Characters as desired by recipient.
Characters as desired by recipient. -
 Sample supplier can be a person of her own choice.
Sample supplier can be a person of her own choice.
-
 The child will be legitimate child of the couple.
The child will be legitimate child of the couple. -
 He/she will have identical legal rights.
He/she will have identical legal rights. -
 The birth certificate shall bear the name of the parent/ parents.
The birth certificate shall bear the name of the parent/ parents. -
 The child upon reaching the age of 18 may demand any information regarding his parentage (except identification).
The child upon reaching the age of 18 may demand any information regarding his parentage (except identification). -
 The child shall have a legal right to parental support, inheritance and all other privileges of a child born to a couple through sexual intercourse.
The child shall have a legal right to parental support, inheritance and all other privileges of a child born to a couple through sexual intercourse.
Since 1993, ICSI is replacing DI and current demand for DI is sharply decreasing. Although ICSI is more and invasive, exhaustive, it helps to achieve biological pregnancy in man with poor sperm, low motility and even in obstructed azoospermia. However, cost is only limiting factor.
DI VS Adoption or Child Free LivingAdoption/child free living are the other viable options. The couple should be discussed before perusing the DI. They should be advised to prefer child free living if genetic concerns dominate. However, if urge to parenting dominates adoption should be preferred.





